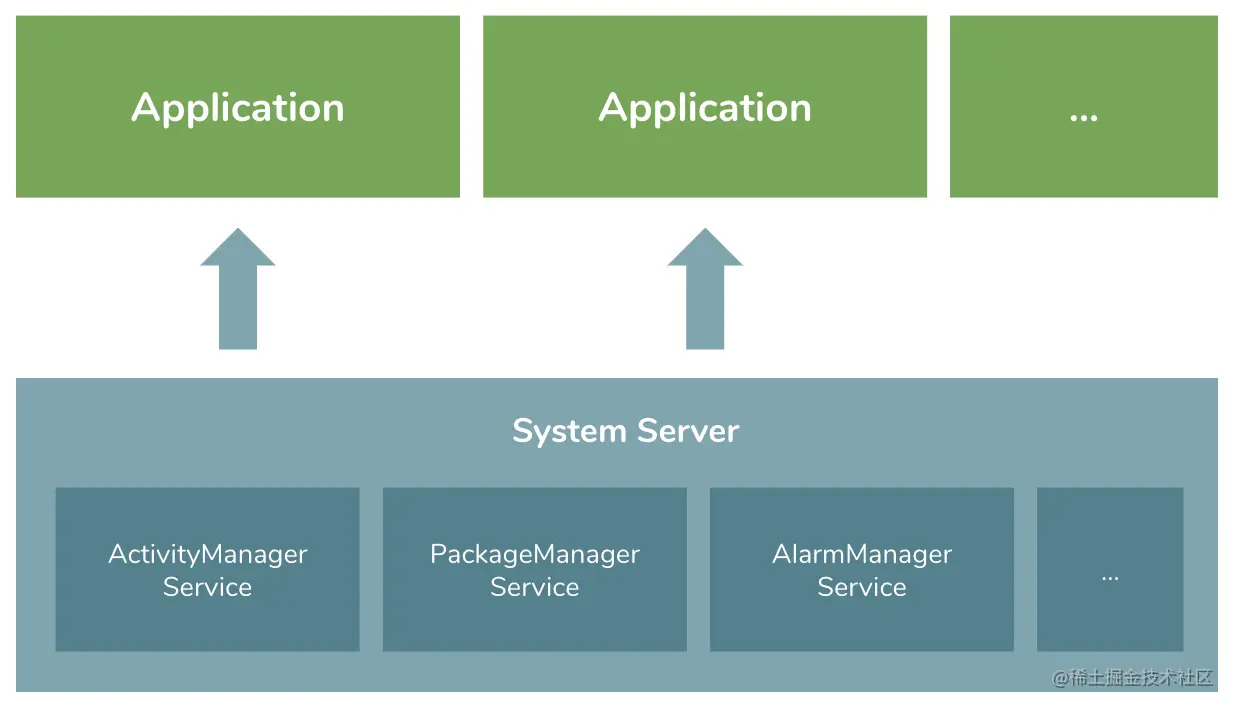
什么是系统 Services?
从 Android 应用的角度来说,系统启动之后,会在一个名为 system_server 的进程中启动一系列的 Services,以向每个进程应用(Application Process)提供各式各样的“服务”,每个 Service 各思其职。比如,大家最熟悉的 Activity 以及其他组件,其生命周期则是由 ActivityManagerService 这个服务来管理的。
而对于开发者而言,在一个普通应用的开发过程中,和系统机制有关的功能都是由这些系统服务来提供实现的。换句话说,我们大部分时候所实现的功能本质上都是在和这些系统服务“打交道”。为了方便开发者使用,Android SDK 内对每个系统 Service 都做了一定程度的封装,提供了必要的 API 来调用。
比如,开发中常用到,设置一个定时闹钟任务:
PendingIntent pi = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT);
AlarmManager alarmManager = (AlarmManager) getSystemService(Service.ALARM_SERVICE);
alarmManager.set(AlarmManager.RTC_WAKEUP, System.currentTimeMillis() + 5 * 1000, pi);
在这里,当前应用进程是通过 AlarmManager 来实现设置定时闹钟,其背后是调用了 AlarmManagerService 来实现相关操作。
系统 Services 的整体流程
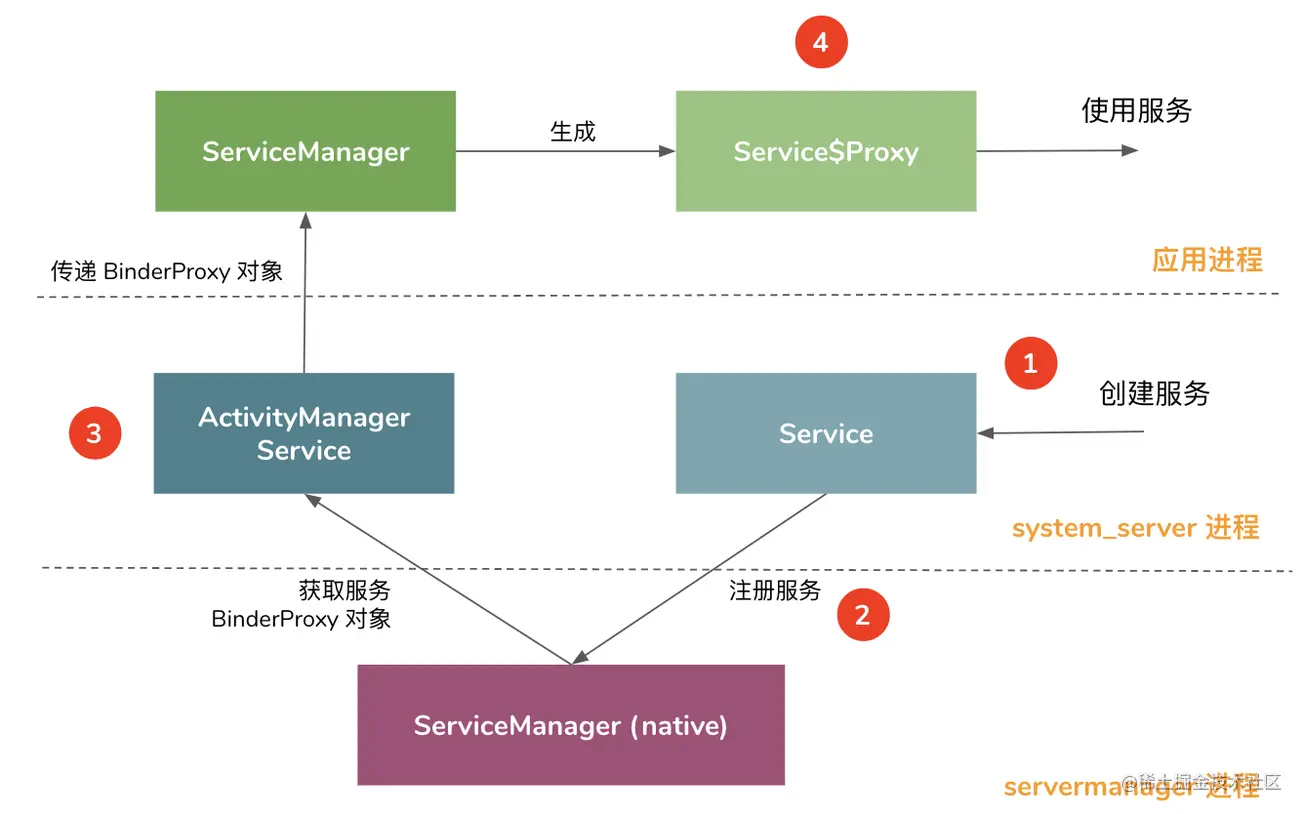
系统 Services 从创建到使用的整体流程示意如下:
其中,整个流程,可分为以下四个步骤(分别对应上图中的数字处):
1、系统 Service 在 system_server 进程中创建、启动;
2、系统 Service 发布 Binder Service 至 Native Framework 的 ServiceManager 中;
3、在应用启动的过程中,ActivityManagerService 从 ServiceManager(native)中获取其他常用的服务(BinderProxy 对象),传递到应用进程的 ServiceManager(java) 中;
4、应用进程中创建各个使用服务的 Manager 对象,如 WindowManager 等,通过上下文 Context 调用使用。
下面的部分会通过源码示例的方式,把以上四个步骤具体流程、实现方式深入分析一下,读者可根据自己想要了解的部分自行跳转阅读,目录在右侧 👉 可找到 。
- 涉及到的源码文件有:
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/sever/
- SystemServer.java
- SystemServiceManager.java
- AlarmManagerService.java
- am/ActivityManagerService.java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/
- ServiceManager.java
- ServiceManagerNative.java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/
- ActivityThread.java
- ContextImpl.java
- SystemServiceRegistry.java
frameworks/native/libs/binder/
- IServiceManager.cpp
frameworks/native/cmds/servicemanager/
- ServiceManager.h
- ServiceManager.cpp
注:源码部分用的 Android 10(Q)版本的,不同的 Android 系统版本在实现的方式存在一定的差异,但整体流程是一样的。
系统 Services 的创建、启动
system_server 进程创建后,在SystemServer 中的 main 方法为入口,依次启动各 Services。
- SystemServer.java
...
// SystemServer 进程主方法入口
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
private void run() {
...
// 创建 SystemServiceManager,用于后续管理系统 Services
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setStartInfo(mRuntimeRestart,
mRuntimeStartElapsedTime, mRuntimeStartUptime);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
...
// Start services.
startBootstrapServices();
// 启动系统电池、GPU 等核心服务
startCoreServices();
// 大部分应用直接所需的服务在此启动
startOtherServices();
...
}
private void startOtherServices() {
...
// 启动 AlarmManagerService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(new AlarmManagerService(context));
...
// 启动 ActivityManagerService
mActivityManagerService = ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.startService(
mSystemServiceManager, atm);
// 启动其他的 Services
...
}
...
其中,不同的 Service 的创建过程会有一定的差异,有的是直接 new 出一个对象,有的通过反射的形式创建,有得需要注册回调等,但核心的流程是一样的。
在 Service 对象创建之后,回调其父类 SystemService onStart 方法,这样一个 Service 就算启动了。
- SystemServiceManager.java
...
private final ArrayList<SystemService> mServices = new ArrayList<SystemService>();
// 启动系统服务
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
// 添加 service 对象到一个 List 中
mServices.add(service);
...
// 回调 onStart
try {
service.onStart();
} ...
}
注册 Binder Service
到此,一个系统 Service 还没有真正的完成注册。所有的 Services 对象是创建在 system_server 进程的,然后通过 Binder 与每一个应用进程进行跨进程通信(IPC),因此需要发布一个 Binder Service,以 AlarmManagerService 为例:
- AlarmManagerService.java
class AlarmManagerService extends SystemService {
...
// 创建一个 IBinder Service 对象,用于实现 Binder 通信
private final IBinder mService = new IAlarmManager.Stub() {
// 设置定时闹钟的接口实现
@Override
public void set(String callingPackage, int type, long triggerAtTime, ...) {
...
setImpl(type, triggerAtTime, ...);
}
...
}
// 设置定时闹钟真正方法入口
void setImpl(int type, long triggerAtTime, ...) {
...
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
...
// onStart 回调中发布该 Binder Service
publishBinderService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE, mService);
}
// 通过 ServiceManager 添加 Binder Service
protected final void publishBinderService(String name, IBinder service,
boolean allowIsolated, int dumpPriority) {
ServiceManager.addService(name, service, allowIsolated, dumpPriority);
}
...
}
ServiceManager 主要用于 Service 的添加与获取。
- ServiceManager.java
...
public static void addService(String name, IBinder service, boolean allowIsolated,
int dumpPriority) {
try {
// 添加一个 Service,这里同样是 IPC 通信
getIServiceManager().addService(name, service, allowIsolated, dumpPriority);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in addService", e);
}
}
private static IServiceManager getIServiceManager() {
if (sServiceManager != null) {
return sServiceManager;
}
// 找到 ServiceManager 对象
// BinderInternal.getContextObject() 为 native 方法,
// 返回指向 IServiceManager 的 BinderProxy 对象
sServiceManager = ServiceManagerNative
.asInterface(Binder.allowBlocking(BinderInternal.getContextObject()));
return sServiceManager;
}
...
接着,往下看 ServiceManagerNative:
- ServiceManagerNative.java
public final class ServiceManagerNative {
...
public static IServiceManager asInterface(IBinder obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return null;
}
// ServiceManager 的代理对象
return new ServiceManagerProxy(obj);
}
// 这里等同于 IServiceManager$Stub$Proxy
class ServiceManagerProxy implements IServiceManager {
public ServiceManagerProxy(IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
mServiceManager = IServiceManager.Stub.asInterface(remote);
}
// 获取服务
public IBinder getService(String name) throws RemoteException {
return mServiceManager.checkService(name);
}
// 添加服务
public void addService(String name, IBinder service, boolean allowIsolated, int dumpPriority)
throws RemoteException {
mServiceManager.addService(name, service, allowIsolated, dumpPriority);
}
}
}
从这里可以看到,发布一个 Service 的过程本身也是 Binder IPC 的方式实现的,最终会传递到 servicemanager 进程中,在 IServiceManager.cpp 内:
- IServiceManager.cpp
class BpServiceManager : public BpInterface<IServiceManager>
{
public:
explicit BpServiceManager(const sp<IBinder>& impl)
: BpInterface<IServiceManager>(impl),
mTheRealServiceManager(interface_cast<AidlServiceManager>(impl))
{
}
// 添加 Service 到 ServiceManager
status_t addService(const String16& name, const sp<IBinder>& service,
bool allowIsolated, int dumpsysPriority) override {
Status status = mTheRealServiceManager->addService(String8(name).c_str(), service, allowIsolated, dumpsysPriority);
return status.exceptionCode();
}
...
}
这里,Native Framework 中的 ServiceManager 是整个 Binder IPC 架构的服务中心,所有大大小小的 service 都需要经过 ServiceManager 来管理
- ServiceManager.h
...
private:
// 定义 Service 的结构体
struct Service {
sp<IBinder> binder; // not null
bool allowIsolated;
int32_t dumpPriority;
};
...
using ServiceMap = std::map<std::string, Service>;
// 用于保存添加进来的 Services
ServiceMap mNameToService;
...
};
- ServiceManager.cpp
Status ServiceManager::addService(const std::string& name, const sp<IBinder>& binder, bool allowIsolated, int32_t dumpPriority) {
...
// 添加 Service 到 mNameToService 中,完成 Binder Service 注册过程
mNameToService[name] = Service {
.binder = binder,
.allowIsolated = allowIsolated,
.dumpPriority = dumpPriority,
};
auto it = mNameToCallback.find(name);
if (it != mNameToCallback.end()) {
for (const sp<IServiceCallback>& cb : it->second) {
// permission checked in registerForNotifications
cb->onRegistration(name, binder);
}
}
return Status::ok();
}
获取并传递 Service 代理对象
在新启动一个应用的过程中,创建应用进程之后,ActivityManagerService 中会获取并缓存常用的系统 Services,通过回调 IApplicationThread.bindApplication() 方法传递 Service 的 BinderProxy 对象到应用进程中去。
- ActivityManagerService.java
// IActivityManager 的 server 端实现
@Override
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread, long startSeq) {
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
// 这里 thread 实际为 IApplicationThread$Stub$Proxy 对象,
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid, callingUid, startSeq);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
@GuardedBy("this")
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid, int callingUid, long startSeq) {
...
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers,
...
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated), // 获取各常用服务
...);
...
return true;
}
private ArrayMap<String, IBinder> getCommonServicesLocked(boolean isolated) {
...
if (mAppBindArgs == null) {
mAppBindArgs = new ArrayMap<>();
// 添加常用的服务进一个 map 中
addServiceToMap(mAppBindArgs, "package");
addServiceToMap(mAppBindArgs, Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
addServiceToMap(mAppBindArgs, Context.ALARM_SERVICE);
addServiceToMap(mAppBindArgs, Context.DISPLAY_SERVICE);
...
}
return mAppBindArgs;
}
private static void addServiceToMap(ArrayMap<String, IBinder> map, String name) {
// 通过 ServiceManager 获取服务
final IBinder service = ServiceManager.getService(name);
if (service != null) {
map.put(name, service);
if (false) {
Log.i(TAG, "Adding " + name + " to the pre-loaded service cache.");
}
}
}
通过 ServiceManager 来获取 Service 的过程和添加一个 Service 的流程是一样的,最终从 Native Framework 中的 ServiceManager 获取到该服务的 BinderProxy 对象。
IApplicationThread 的 server 端实现在 ActivityThread 中:
- ActivityThread.java
public final class ActivityThread extends ClientTransactionHandler {
...
private class ApplicationThread extends IApplicationThread.Stub {
// 传递指向系统 Service 的 BinderProxy 对象
public final void bindApplication(..., Map services, ...) {
if (services != null) {
...
// 添加进应用进程的 ServiceManager 中
ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services);
}
}
}
}
- ServiceManager.java
public static void initServiceCache(Map<String, IBinder> cache) {
if (sCache.size() != 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("setServiceCache may only be called once");
}
// 存进 cache
sCache.putAll(cache);
}
使用系统 Services
Context 上下文提供了 getSystemService 接口调用,Context 的真正实现类是 ContextImpl:
- ContextImpl.java
...
@Override
public Object getSystemService(String name) {
return SystemServiceRegistry.getSystemService(this, name);
}
SystemServiceRegistry 负责根据 ServiceManager 中各 Service 的 BinderProxy 来创建 Binder 通信的 client 端对象,并封装在对应的 Manager 对象。
- SystemServiceRegistry.java
// 管理{@link ContextImpl#getSystemService} 可以返回的所有系统服务
final class SystemServiceRegistry {
...
private static final Map<Class<?>, String> SYSTEM_SERVICE_NAMES =
new ArrayMap<Class<?>, String>();
private static final Map<String, ServiceFetcher<?>> SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS =
new ArrayMap<String, ServiceFetcher<?>>();
...
// SystemServiceRegistry 类被加载时创建各 Manager 对象
static {
registerService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE, AlarmManager.class,
new CachedServiceFetcher<AlarmManager>() {
@Override
public AlarmManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) throws ServiceNotFoundException {
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getServiceOrThrow(Context.ALARM_SERVICE);
IAlarmManager service = IAlarmManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return new AlarmManager(service, ctx);
}});
...
registerService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, ActivityManager.class,
new CachedServiceFetcher<ActivityManager>() {
@Override
public ActivityManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) {
return new ActivityManager(ctx.getOuterContext(), ctx.mMainThread.getHandler());
}});
...
}
private static <T> void registerService(String serviceName, Class<T> serviceClass,
ServiceFetcher<T> serviceFetcher) {
SYSTEM_SERVICE_NAMES.put(serviceClass, serviceName);
SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS.put(serviceName, serviceFetcher);
}
// 返回系统 Service 对应的 Manager 对象
public static Object getSystemService(ContextImpl ctx, String name) {
ServiceFetcher<?> fetcher = SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS.get(name);
return fetcher != null ? fetcher.getService(ctx) : null;
}
}
- ServiceManager.java
public static IBinder getServiceOrThrow(String name) throws ServiceNotFoundException {
final IBinder binder = getService(name);
if (binder != null) {
return binder;
} else {
throw new ServiceNotFoundException(name);
}
}
public static IBinder getService(String name) {
try {
// 各常用服务的代理对象已放入缓存,直接从缓存中取
IBinder service = sCache.get(name);
if (service != null) {
return service;
} else {
// 其他非常用服务则再 通过 Binder IPC 来获取
return Binder.allowBlocking(rawGetService(name));
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in getService", e);
}
return null;
}
private static IBinder rawGetService(String name) throws RemoteException {
...
final IBinder binder = getIServiceManager().getService(name);
...
return binder;
}
到此,整个系统 Services 的流程的代码示例已经展示完。
总结 & 拓展
- 系统 Services 是 Android Framework 中最为重要、核心的部分,也是 Android 进阶开发者必须要学习的部分。
- 系统 Services 的整体相关流程可大致分为 创建&启动、注册 Binder Service、获取&传递代理对象、使用 Service 这四个步骤。
- 在每一个层级的进程中,都会有一个
ServiceManager对象来管理系统 Services(或代理对象),用户进程和system_server进程中的为 java 对象(对应同一个 ServiceManager.java),severmanager进程则为 native 对象(service_manager.c 或 ServiceManager.cpp),也是整个 Binder 架构的服务管理中心。 - 整体流程中大量涉及到 Binder IPC 的运用,Binder 是 Android Framework 中最重要也是较难理解的 IPC 机制,对此有一定了解才能顺利地阅读相关代码。
- 本文介绍的系统 Services 代表的是 Java Framework 层所提供的 Services,严格意义上还有 C++ Framework 中提供的 Media 相关的服务,不再本文的讨论范围内。
- 每个系统 Services 内都有各自众多复杂机制的实现,可根据自身想要了解的部分再去深入阅读相关代码。